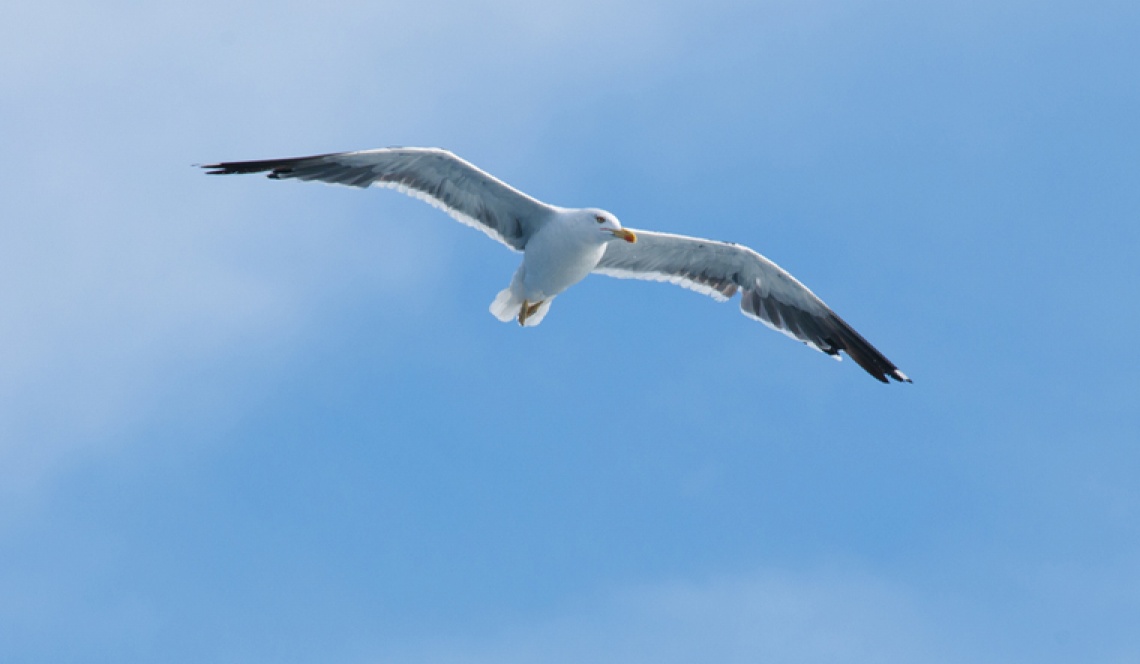
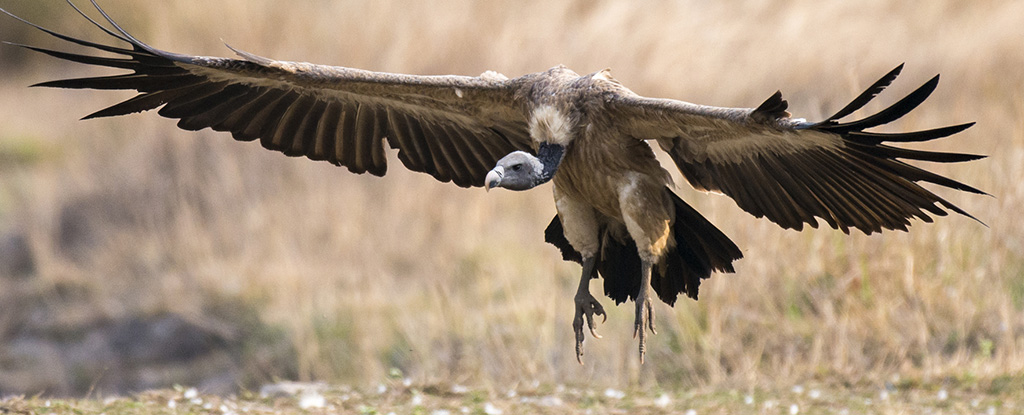
Predator-prey equilibria are being disrupted by climate change, according to a study led by Brazilian researchers and published in Nature Climate Change. Credit: Mythilibadam/ Wikimedia Commons
Predator-prey equilibria are being disrupted by climate change, according to a study led by Brazilian researchers and published in Nature Climate Change. Credit: Mythilibadam/ Wikimedia Commons
Feb. 22, 2019 (Phys.org) -- With herbivores, omnivores, carnivores, insectivores, frugivores, scavengers and decomposers, Earth's ecosystems function within a vast web of interactions among plants, animals, insects, fungi and microorganisms. A fundamental part of this web resides in the equilibrium of the food chain that links predators to herbivores and regulates plant production on our planet.
Equilibria between predators and plant-feeding prey may be disrupted by future climate change, according to a study published in Nature Climate Change. "The study describes the causes of this disruption and shows it can be explained by the components of climate that will change in future, especially temperature," said Gustavo Quevedo Romero, a professor at the University of Campinas's Biology Institute (IB-UNICAMP) in São Paulo State, Brazil, and lead author of the article.
The study concluded that climate change can redistribute the strength of ecological interactions between predator and prey species. The results show that higher temperatures and a more stable climate with less seasonal variability lead to more intense predation pressure.
(more)
READ MORE: Phys.org